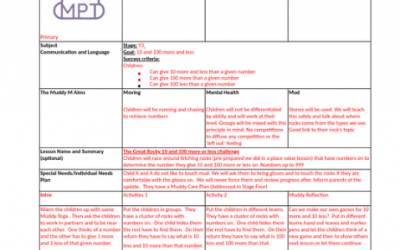
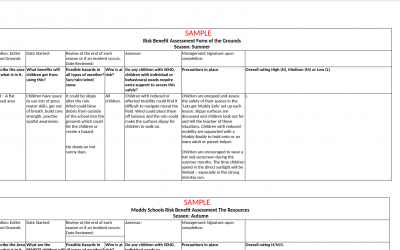
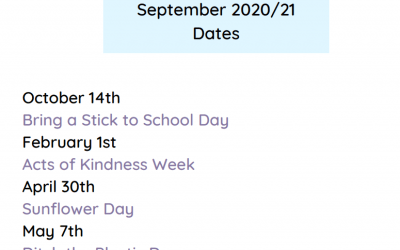
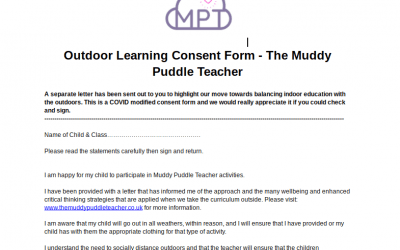
Use EYFS outdoor lesson plan Sample as part of Stage Two in the accredited training programme.
Outdoor Learning Risk Benefit
Oct 5, 2020
Use Muddy Risk Benefit as part of your accredited training tasks. Use this as a sample to show the risks and benefits to those risks.
Muddy Puddle Teacher Handbook
Oct 5, 2020
Use Muddy School Policies as part of evidence for the accredited stage one process of the training. This policy will help you develop good standards and practice to our approach.
The Great Muddy Audit
Oct 5, 2020
The Great Muddy Audit is for those engaged with stage one of the MPT accredited training. It allows trainees to reflect on their training and make the most of their outdoor spaces.
*FRee*Outdoor Learning Dates Poster
Sep 6, 2020
Join in with some Outdoor Learning Days to keep the momentum going and have this Outdoor Learning Dates Poster 20/21...
Outdoor Learning Parent Safety Information Sheet
Sep 4, 2020
Use our Outdoor Learning Parent Safety Information Sheet to help update your parents on safe, fun routines when out and about.
Outdoor Learning Parent Consent Form
Sep 4, 2020
Use our Parent Consent Form to inform and get permission from parents to use our much loved outdoor learning approach.
Outdoor Learning COVID Support Pack
Sep 2, 2020
Let us help with our Outdoor Learning COVID Support Pack to give you guidance and reassurance of best practice when outside.
Letter to Parents – Welcome to MPT
Sep 2, 2020
Use Letter to parents - Welcome to MPT to inform parents of your move to a more muddy and merry curriculum. Our muddy...
Outdoor Progress Tracker (whole school)
Jul 17, 2020
Progress Tracker – all ages
Outdoor Sample Lesson Plan – Planning
Jul 17, 2020
Sample Lesson Plan – Planning
Outdoor care plan (Individual and SEND)
Jul 17, 2020
Outdoor care plan
Outdoor Learning Goal Setting
Jul 17, 2020
Use the Muddy Goal Setting to help you set targets and plan for developing your outdoor space.
Great Muddy Plan
Jul 2, 2020
Use the Great Muddy Plan to help you set up a more natural outdoor space.
New In

8 Year Three Big Write Ideas Outdoors

8 Year Two Big Write Ideas Outdoors
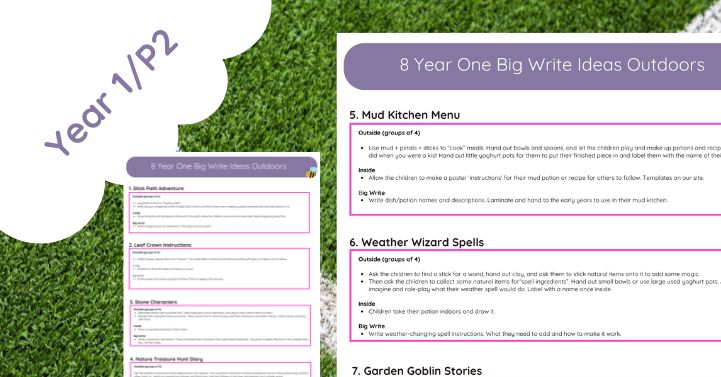
8 Year One Big Write Ideas Outdoors

8 Early Years Big Write Ideas Outdoors

Open Day Outdoor Learning Parent Packs ( Muddy Trained Schools)

10 Outdoor Activity Ideas for Wheels on the Bus
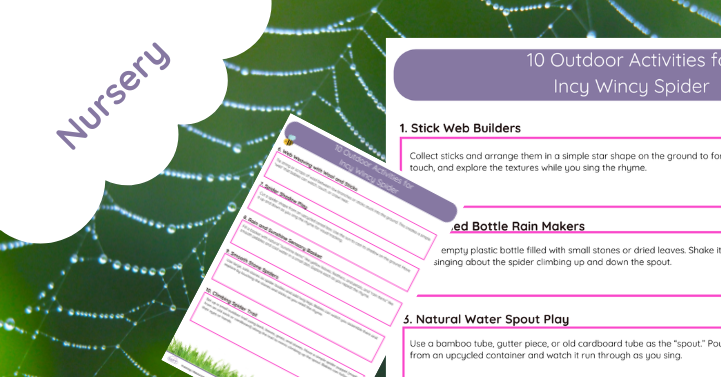
10 Outdoor Activities for Incy Wincy Spider

10 Outdoor Hey Diddle Diddle Activity Ideas
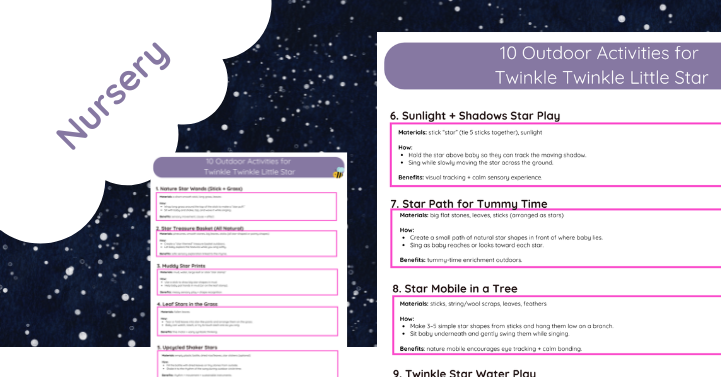
10 Outdoor Activities for Twinkle Twinkle Little Star